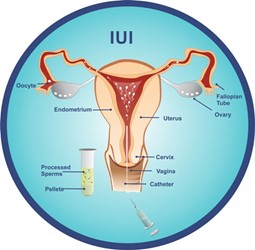
Intrauterine insemination, or IUI is a fertility treatment that involves placing your partner’s processed sperm sample inside your womb, at the time of ovulation to facilitate fertilisation.
This procedure can be performed during a natural ovulation or with hormone stimulation known as Super Ovulation with IUI (SO-IUI).
IUI is a less invasive and less expensive option as compared to IVF ( in-vitro fertilisation)
The aim of IUI is to isolate and concentrate the number of motile sperm and to shorten the distance for them to reach the egg resting in the fallopian tube and increase the chances of fertilisation.
IUI may help couples who are diagnosed with:
- Unexplained infertility
- Moderate low sperm count and moderate low number of motile sperm
- Cervical mucus/scar problems
- Erectile dysfunction
- Non-consummation
IUI is not suitable in couples with
- Woman with disease of the fallopian tube
- Male partner with severe low count and motile sperm
Success Rate
The success rate after IUI varies from 15% to 20% depending on various factors such as the age of a woman, cause, and duration of infertility.
Since IUI is a simpler and less invasive procedure than an IVF, it can be a good first option for fertility treatment with a reasonable success rate. However, if you have had three or more unsuccessful attempts with IUI, or if you are aged 35 or over, you are more likely to have a greater chance of success with IVF.
Risks
-A small risk of pelvic infection may occur after IUI.
-The risk of multiple pregnancies is also present when 3-4 eggs develop when hormones are used in SO-IUI.
-You may be counselled to cancel the IUI cycle if there is risk of multiple pregnancy developing
Costs
Estimated costs for IUI, vary among patients, depending on additional investigations, medications, and doctor consultations.
IUI Steps
- The IUI procedure starts by monitoring the woman’s cycle to determine the day of ovulation
- Once the follicle is mature, ovulation either occurs naturally or is triggered by an injection of a stimulation drug.
- Husband submits semen sample which is washed in the lab to isolate good motile sperm.
- Finally, the processed sperm is injected directly into the uterine cavity using a catheter generally within 24 hours of ovulation.